Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly transforming the job market, with skills such as data engineering, data science, and machine learning becoming integral across industries. However, the development and application of AI varies by region, influenced by the dominant industries and economic priorities of each area. This report focuses on the use of AI skills in California and Tennessee, two states with contrasting economies and job markets. California, known for its tech-centric economy and innovation hubs like Silicon Valley, is hypothesized to leverage AI for advanced technical and research roles. Meanwhile, Tennessee, with its focus on healthcare, manufacturing, and business services, is expected to utilize AI for business process improvement and operational efficiency. Through an exploration of AI job distributions, skill applications, and career area trends, this research aims to shed light on how AI skills are employed in these two distinct markets.
A Tale of Two Cities: An AI Driven Workplace – Explore Interactive Data
According to the AI density map constructed by our team, California and Texas are the two states with the highest number proportion of AI job postings. Therefore, we selected California as a suitable benchmark for our analysis.
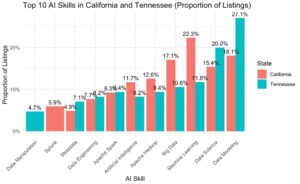
If we look at the top 10 AI skills across the two states (2010-2023 period), we can see large gaps on three skills categories, namely, data modelling, data science and machine learning. For example, the proportion of jobs requiring data modelling skills in Tennessee is 27% versus 18.1% in California. Data modelling skills requires expertise in both technology and business activities with clear benefits in process improvement, decision making and cost reduction. Similarly, the gap in job posting proportion for the data science skill is roughly around 4.6%. This skill requires a mix of mathematics, programming and domain-specific knowledge to transform raw data into specific insights for improved decision making. Nevertheless, the largest gap in AI job listings is in the machine learning skill where California registers 22.3% of job listings requiring this skill whereas Tennessee registers only 11.8%.
Although it is true that there is some overlap among these top 3 AI skills, the machine learning skill requires a higher degree of technical expertise. This skill not only requires the development of statistical models for business applications, but it also requires the development of algorithms for both supervised and unsupervised tasks. This skill includes the development of AI technologies, and improving existing algorithmic specifications, on top of applying existing methods to business applications. Common job postings requiring this skill in California include ML engineer, software engineer, data engineering, and others.
Considering a most recent time period (2020-2023), we find that skills such as deep learning, pytorch (ML library), and tensorflow have a greater listing proportion in California as compared to Tennessee. In contrast, some other skills such as data analysis are more predominant in the state of Tennessee. These findings reaffirms the observation that California based AI job postings have a greater focus on deeper technical expertise in AI as compared to Tennessee based job postings.
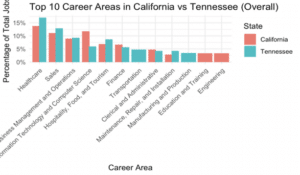
If we take a look at the most popular career areas requiring AI jobs, we find some interesting insights across the two states. On the one hand, Tennessee has a greater proportion of job listings requiring AI jobs in career areas such as sales, healthcare and manufacturing. On the other hand, California has a greater proportion of AI jobs in IT, education and engineering.
Based on the analysis, there is some evidence to support the hypothesis that AI skills in California are more focused on advanced technical and research-oriented roles, such as data engineering, data science, and software engineering, while in Tennessee, AI skills are more commonly applied to business analysis and process improvement roles, like Business Intelligence analysts and sales engineers.
Furthermore, data shows that career areas where AI is implemented more as a tool for process improvement and operational support—such as Marketing, HR, Healthcare, Manufacturing, and Maintenance—have a higher proportional representation in Tennessee. Conversely, career areas where AI is employed for innovation, research, and advanced development—such as IT and Computer Science, Engineering, and Science and Research—are more prominent in California.
These findings support the theory that while California serves as a hub for innovation-driven AI adoption—fostering new technologies and encouraging experimentation—Tennessee takes a complementary approach, emphasizing practical, process-oriented AI integration. In California, AI advancements are often geared toward breakthrough innovations and industry disruption, whereas in Tennessee, AI is strategically leveraged to enhance operational efficiencies and modernize traditional industries. Both states showcase distinct but equally significant contributions to the evolving AI landscape.
A Tale of Two Cities: An AI Driven Workplace – Explore Interactive Data
The job postings are provided by Lightcast.